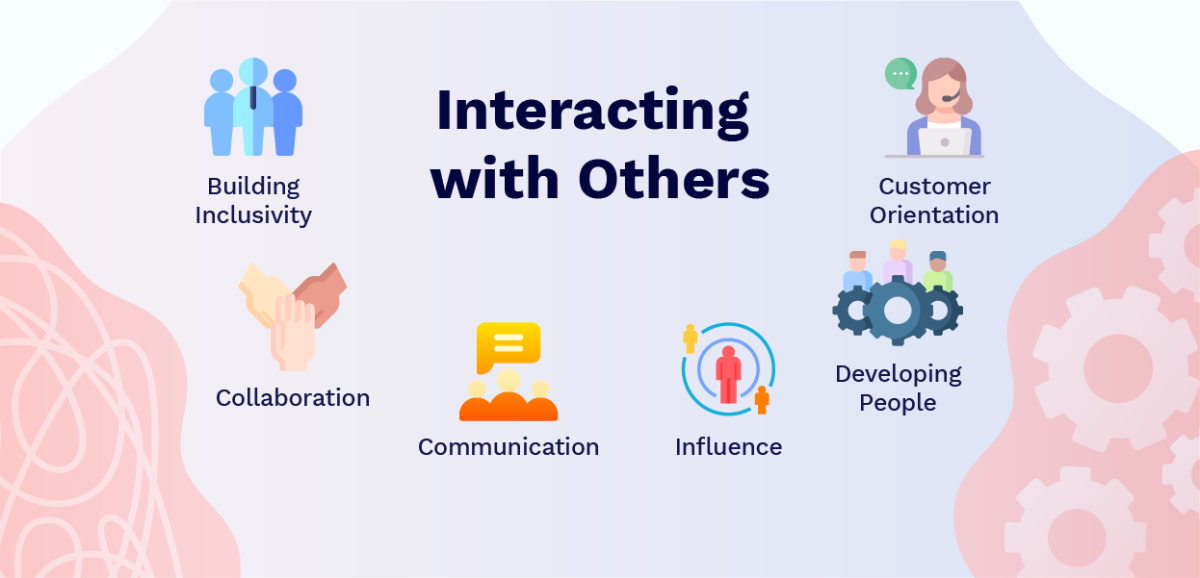
The ‘Interacting with Others’ cluster has all to do with people relations. Learning from other individuals is one of the most effective ways to acquire new skills and ideas.
Effective interaction with others means putting others’ needs first, being open to exchanging ideas and building a shared understanding of a problem or situation.
Building Inclusivity
represents the skill to manage relationships across diverse groups within an organisation. Individuals with this skill are sensitive towards the differences in diversity dimensions and perspectives such as race, religion, gender orientation, age and more. These individuals seek to establish a common ground among stakeholders and often seek out their best interests.
Collaboration
is being cooperative and a good team player. Collaborative individuals create synergies with others and build effective relationships across the organisation. They are accommodating to different working styles and often seek out win-win outcomes to achieve goals.
Communication
encompasses the art of conveying and exchanging information effectively and clearly. People who are well versed in communication skills can synthesise their responses to suit different audiences through various mediums and approaches. They are able to facilitate two-way interactions, identify and overcome communication gaps as well.
Customer Orientation
is the ability to build relationships with customers, both internal and external, to anticipate their needs and solicit feedback to deliver an effective customer experience. These are individuals with great interpersonal and problem-solving skills. They are often able to identify areas of improvement and appropriate service recovery interventions.
Developing People
demonstrates a leadership quality that seeks to empower themselves and others to learn, and develop their strengths to enhance performance. People with this skill take delight in coaching and supporting co-workers to foster a conducive environment of enablement. They do so with the end motive of achieving personal or organisation goals.
Influence
comes from the ability to demonstrate empathy and communicate well. These individuals tend to have high emotional intelligence. They are able to build effective relationships with people and influence behaviours, beliefs or attitudes to achieve desired outcomes.